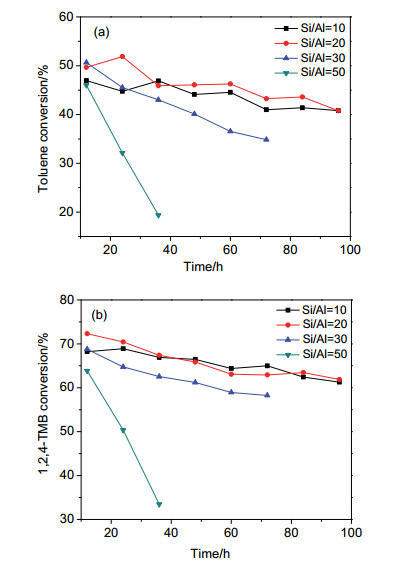
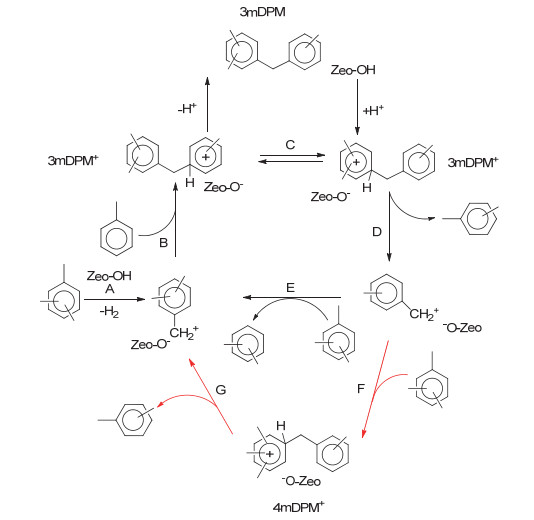
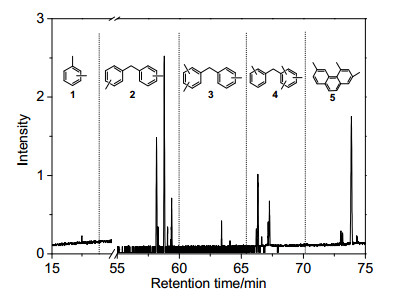
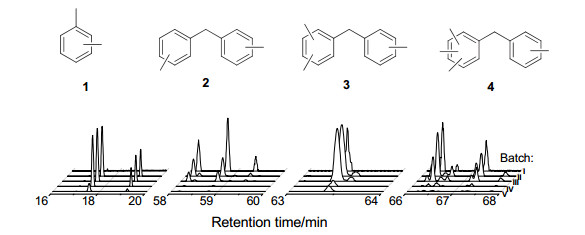
-
[1]
Tsai, T.-C.; Liu, S.-B.; Wang, I. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 181, 355.
doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(98)00396-2
-
[2]
Xu, O.; Su, H.; Ji, J.; Jin, X.; Chu, J. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 15, 326.
doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(07)60088-3
-
[3]
Tukur, N. M.; Al-Khattaf, S. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2499.
doi: 10.1021/ef7002602
-
[4]
Chen, Q. L.; Kong, D. J.; Yang, W. S. Petrochem. Technol. 2004, 33, 909.
-
[5]
Hamedi, N.; Iranshahi, D.; Rahimpour, M. R.; Raeissi, S.; Rajaei, H. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 48, 56.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2014.10.015
-
[6]
Ali, S. A.; Ogunronbi, K. E.; Al-Khattaf, S. S. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 2601.
doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2013.04.014
-
[7]
Ali, S. A.; Aitani, A. M.; Ercan, C.; Wang, Y.; Al-Khattaf, S. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 2125.
doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2011.01.031
-
[8]
Tsai, T.-C.; Liu, S.-B.; Wang, I. Catal. Surv. Asia 2009, 13, 94.
doi: 10.1007/s10563-009-9070-z
-
[9]
-
[10]
Chen, N. Y.; Degnan, T. F. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1988, 84, 32.
-
[11]
Lee, Y.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Rhee, H.-K. Catal. Today 1998, 44, 223.
doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00194-1
-
[12]
Chao, K.-J.; Leu, L.-J. Zeolites 1989, 9, 193.
doi: 10.1016/0144-2449(89)90025-0
-
[13]
Krejčí, A.; Al-Khattaf, S.; Ali, M. A.; Bejblová, M.; Čejka, J. Appl. Catal., A 2010, 377, 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.01.026
-
[14]
Yue, Y. H.; Tang, Y.; Kan, Y. Z.; Gao, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 1996, 54, 591.
-
[15]
Meshram, N. R.; Kulkarni, S. B.; Ratnasamy, P. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., Chem. Technol. 1984, 34, 119.
-
[16]
Ji, Y. J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Peng, H. G.; Wu, P. 1980, 38, 191.(纪永军, 张斌, 张坤, 徐乐, 彭洪根, 吴鹏, 化学学报, 1980, 38, 191.)
-
[17]
Higgins, J. B.; LaPierre, R. B.; Schlenker, J. L.; Rohrman, A. C.; Wood, J. D.; Kerr, G. T.; Rohrbaugh, W. J. Zeolites 1988, 8, 446.
doi: 10.1016/S0144-2449(88)80219-7
-
[18]
Hegde, S. G.; Kumar, R.; Bhat, R. N.; Ratnasamy, P. Zeolites 1989, 9, 231.
doi: 10.1016/0144-2449(89)90031-6
-
[19]
Wang, I.; Tsai, T. C.; Huang, S. T. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 2005.
-
[20]
Dumitriu, E.; Hulea, V.; Kaliaguine, S.; Huang, M. M. Appl. Catal., A 1996, 135, 57.
doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(95)00236-7
-
[21]
Corma, A.; Llopis, F.; Monton, J. B. J. Catal. 1993, 140, 384.
doi: 10.1006/jcat.1993.1092
-
[22]
Al-Khattaf, S.; Ali, S. A.; Aitani, A. M.; Zilkova, N.; Kubicka, D.; Cejka, J. Catal. Rev.: Sci. Eng. 2014, 56, 333.
doi: 10.1080/01614940.2014.946846
-
[23]
Corma, A.; Sastre, E. J. Catal. 1991, 129, 177.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(91)90021-U
-
[24]
Xiong, Y.; Rodewald, P. G.; Chang, C. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9427.
doi: 10.1021/ja00142a007
-
[25]
Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U.; Lillerud, K.-P.; Kolboe, S.; Bjørgen, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5618.
doi: 10.1021/ja060931w
-
[26]
Li, Y. C.; Wang, H.; Dong, M.; Li, J. F.; Qin, Z. F.; Wang, J. G.; Fan, W. B. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 66301.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA09236A
-
[27]
Newsam, J.; Treacy, M. M.; Koetsier, W.; De Gruyter, C. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1988, 420, 375.
doi: 10.1098/rspa.1988.0131
-
[28]
Min, H.-K.; Chidambaram, V.; Hong, S. B. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 1190.
doi: 10.1021/jp9094408
-
[29]
Byun, Y.; Jo, D.; Shin, D. N.; Hong, S. B. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1764.
doi: 10.1021/cs500186y
-
[30]
Camblor, M. A.; Mifsud, A.; Pérez-Pariente, J. Zeolites 1991, 11, 792.
doi: 10.1016/S0144-2449(05)80057-0

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: