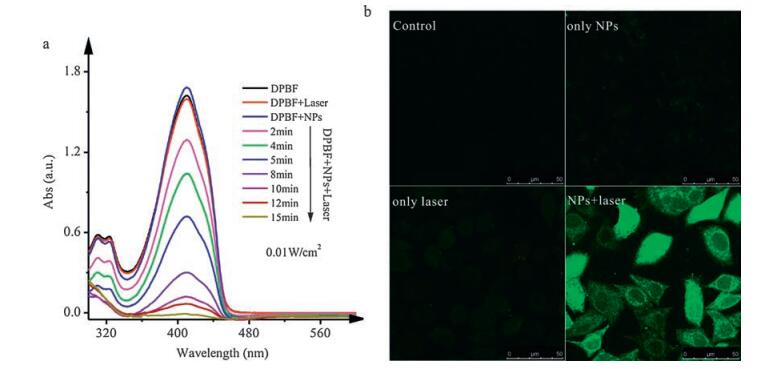
-
[1]
Liu H., Chen D., Li L.. Multifunctional gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles:a platform for the combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy with low systemic toxicity[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,
2011,50:891-895.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201002820
-
[2]
Fang W., Yang J., Gong J.. Photo-and pH-Triggered Release of Anticancer Drugs from Mesoporous Silica-Coated Pd@Ag Nanoparticles[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater.,
2012,22:842-848.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201101960
-
[3]
Wang C., Xu H., Liang C.. Iron oxide@polypyrrole nanoparticles as a multifunctional drug carrier for remotely controlled cancer therapy with synergistic antitumor effect[J]. ACS Nano,
2013,7:6782-6795.
doi: 10.1021/nn4017179
-
[4]
Zheng M., Yue C., Ma Y.. Single-step assembly of DOX/ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy[J]. ACS Nano,
2013,7:2056-2067.
doi: 10.1021/nn400334y
-
[5]
Tang S., Chen M., Zheng N.. Multifunctional ultrasmall Pd nanosheets for enhanced near-infrared photothermal therapy and chemotherapy of cancer[J]. Nano Res.,
2014,8:165-174.
-
[6]
Shi S., Chen X., Wei J.. Platinum(ⅳ) prodrug conjugated Pd@Au nanoplates for chemotherapy and photothermal therapy[J]. Nanoscale,
2016,8:5706-5713.
doi: 10.1039/C5NR09120A
-
[7]
Miao W., Shim G., Lee S.. Safety and tumor tissue accumulation of pegylated graphene oxide nanosheets for co-delivery of anticancer drug and photosensitizer[J]. Biomaterials,
2013,34:3402-3410.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.010
-
[8]
Zhang M., Murakami T., Ajima K.. Fabrication of ZnPc/protein nanohorns for double photodynamic and hyperthermic cancer phototherapy[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.,
2008,105:14773-14778.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801349105
-
[9]
Jang B., Park J.-Y., Tung C.-H.. Gold nanorod-photosensitizer complex for near-infrared fluorescence imaging and photodynamic/photothermal therapy in vivo[J]. ACS Nano,
2011,5:1086-1094.
doi: 10.1021/nn102722z
-
[10]
Wang S., Huang P., Nie L.. Single continuous wave laser induced photodynamic/plasmonic photothermal therapy using photosensitizer-functionalized gold nanostars[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2013,25:3055-3061.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v25.22
-
[11]
Zhao Z.X., Huang Y.Z., Shi S.G.. Cancer therapy improvement with mesoporous silica nanoparticles combining photodynamic and photothermal therapy[J]. Nanotechnology,
2014,25285701.
doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/25/28/285701
-
[12]
Cheng L., Wang C., Feng L.. Functional nanomaterials for phototherapies of cancer[J]. Chem. Rev.,
2014,114:10869-10939.
doi: 10.1021/cr400532z
-
[13]
Sun M., Xu L., Ma W.. Hierarchical plasmonic nanorods and upconversion core-satellite nanoassemblies for multimodal imaging-guided combination Phototherapy[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2016,28:898-904.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v28.5
-
[14]
Tian B., Wang C., Zhang S.. Photothermally enhanced photodynamic therapy delivered by nano-graphene oxide[J]. ACS Nano,
2011,5:7000-7009.
doi: 10.1021/nn201560b
-
[15]
Lin T.Y., Guo W., Long Q.. HSP90 Inhibitor encapsulated phototheranostic nanoparticles for synergistic combination cancer therapy[J]. Theranostics,
2016,6:1324-1335.
doi: 10.7150/thno.14882
-
[16]
Bonnett R.. Photosensitizers of the porphyrin and phthalocyanine series for photodynamic therapy[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev.,
1995,24:19-33.
doi: 10.1039/cs9952400019
-
[17]
Huang X., El-Sayed I.H., Qian W.. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2006,128:2115-2120.
doi: 10.1021/ja057254a
-
[18]
Konan Y.N., Gurny R., Allémann E.. State of the art in the delivery of photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy[J]. J. Photochem. Photobio. B,
2002,66:89-106.
doi: 10.1016/S1011-1344(01)00267-6
-
[19]
Mou J., Lin T., Huang F.. Black titania-based theranostic nanoplatform for single NIR laser induced dual-modal imaging-guided PTT/PDT[J]. Biomaterials,
2016,84:13-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.01.009
-
[20]
Gao L., Fei J., Zhao J.. Hypocrellin-loaded gold nanocages with high twophoton efficiency for photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy in vitro[J]. ACS Nano,
2012,6:8030-8040.
doi: 10.1021/nn302634m
-
[21]
Kah J.C., Wan R.C., Wong K.Y.. Combinatorial treatment of photothermal therapy using gold nanoshells with conventional photodynamic therapy to improve treatment efficacy:an in vitro study[J]. Laser. Surg. Med.,
2008,40:584-589.
doi: 10.1002/lsm.v40:8
-
[22]
Kuo W.S., Chang Y.T., Cho K.C.. Gold nanomaterials conjugated with indocyanine green for dual-modality photodynamic and photothermal therapy[J]. Biomaterials,
2012,33:3270-3278.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.035
-
[23]
Shi S., Zhu X., Zhao Z.. Photothermally enhanced photodynamic therapy based on mesoporous Pd@Ag@mSiO2 nanocarriers[J]. J. Mater. Chem. B,
2013,11133.
doi: 10.1039/c2tb00376g
-
[24]
Zhao Z., Shi S., Huang Y.. Simultaneous photodynamic and photothermal therapy using photosensitizer-functionalized Pd nanosheets by single continuous wave laser[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface,
2014,6:8878-8885.
doi: 10.1021/am501608c
-
[25]
Huang Y., Chen X., Shi S.. Effect of glutathione on in vivo biodistribution and clearance of surface-modified small Pd nanosheets[J]. Sci. China Chem.,
2015,58:1753-1758.
-
[26]
Gollavelli G., Ling Y.C.. Magnetic and fluorescent graphene for dual modal imaging and single light induced photothermal and photodynamic therapy of cancer cells[J]. Biomaterials,
2014,35:4499-4507.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.011
-
[27]
Zhang P., Huang H., Huang J.. Noncovalent ruthenium(Ⅱ) complexessingle-walled carbon nanotube composites for bimodal photothermal and photodynamic therapy with near-infrared irradiation[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,
2015,7:23278-23290.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b07510
-
[28]
Liu T., Wang C., Cui W.. Combined photothermal and photodynamic therapy delivered by PEGylated MoS 2 nanosheets[J]. Nanoscale,
2014,6:11219-11225.
doi: 10.1039/C4NR03753G
-
[29]
Yong Y., Zhou L., Gu Z.. WS2 nanosheet as a new photosensitizer carrier for combined photodynamic and photothermal therapy of cancer cells[J]. Nanoscale,
2014,610394.
doi: 10.1039/C4NR02453B
-
[30]
Tan X., Pang X., Lei M.. An efficient dual-loaded multifunctional nanocarrier for combined photothermal and photodynamic therapy based on copper sulfide and chlorin e6[J]. Int. J. Pharm.,
2016,503:220-228.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.03.019
-
[31]
Wang S., Riedinger A., Li H.. Plasmonic copper sulfide nanocrystals exhibiting near-infrared photothermal and photodynamic therapeutic effects[J]. ACS Nano,
2015,9:1788-1800.
doi: 10.1021/nn506687t
-
[32]
Han L., Zhang Y., Chen X.-W.. Protein-modified hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles carrying indocyanine green for photothermal and photodynamic therapy[J]. J. Mater. Chem. B,
2016,4:105-112.
-
[33]
Huang Y., Lai Y., Shi S.. Copper sulfide nanoparticles with phospholipid-PEG coating for in vivo near-infrared photothermal cancer therapy[J]. Chem. Asian. J.,
2015,10:370-376.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v10.2
-
[34]
Kim Y.K., Na H.K., Kim S.. One-pot synthesis of multifunctional Au@graphene oxide nanocolloid core@shell nanoparticles for Raman bioimaging, photothermal, and photodynamic therapy[J]. Small,
2015,11:2527-2535.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v11.21
-
[35]
Crescenzi E., Varriale L., Iovino M.. Photodynamic therapy with indocyanine green complements and enhances low-dose cisplatin cytotoxicity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. Mol. Cancer. Ther.,
2004,3:537-544.
-
[36]
Wu L., Fang S., Shi S.. Hybrid polypeptide micelles loading indocyanine green for tumor imaging and photothermal effect study[J]. Biomacromolecules,
2013,14:3027-3033.
doi: 10.1021/bm400839b
-
[37]
Taratula O., Schumann C., Duong T.. Dendrimer-encapsulated naphthalocyanine as a single agent-based theranostic nanoplatform for near-infrared fluorescence imaging and combinatorial anticancer phototherapy[J]. Nanoscale,
2015,7:3888-3902.
doi: 10.1039/C4NR06050D
-
[38]
Lim C.K., Shin J., Lee Y.D.. Phthalocyanine-aggregated polymeric nanoparticles as tumor-homing near-infrared absorbers for photothermal therapy of cancer[J]. Theranostics,
2012,2:871-879.
doi: 10.7150/thno.4133
-
[39]
Karan S., Mallik B.. Templating effects and optical characterization of copper (Ⅱ) phthalocyanine nanocrystallites thin film:nanoparticles, nanoflowers, nanocabbages, and nanoribbons[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C.,
2007,111:7352-7365.
doi: 10.1021/jp070302o
-
[40]
Triesscheijn M., Baas P., Schellens J.H.. Photodynamic therapy in oncology[J]. Oncologist,
2006,11:1034-1044.
doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.11-9-1034
-
[41]
Mathew S., Murakami T., Nakatsuji H.. Exclusive photothermal heat generation by a gadolinium bis (naphthalocyanine) complex and inclusion into modified high-density lipoprotein nanocarriers for therapeutic applications[J]. ACS Nano,
2013,7:8908-8916.
doi: 10.1021/nn403384k
-
[42]
Singh A.K., Hahn M.A., Gutwein L.G.. Multi-dye theranostic nanoparticle platform for bioimaging and cancer therapy[J]. Int. J. Nanomed.,
2012,7:2739-2750.
-
[43]
Jin Y., Ye F., Zeigler M.. Near-infrared fluorescent dye-doped semiconducting polymer dots[J]. ACS Nano,
2011,5:1468-1475.
doi: 10.1021/nn103304m
-
[44]
Song L.. Naphthalocyanine-reconstituted LDL nanoparticles for in vivo cancer imaging and treatment[J]. Int. J. Nanomed.,
2007,2:767-774.
-
[45]
Tian Q., Jiang F., Zou R.. Hydrophilic Cu9S5 nanocrystals:A photothermal agent with a 25.7% heat conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells in vivo[J]. ACS Nano,
2011,5:9761-9771.
doi: 10.1021/nn203293t
-
[46]
Roper D.K., Ahn W., Hoepfner M.. Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C,
2007,111:3636-3641.
doi: 10.1021/jp064341w
-
[47]
Ku G., Zhou M., Song S.. Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a new class of photoacoustic contrast agent for deep tissue imaging at 1064nm[J]. ACS Nano,
2012,6:7489-7496.
doi: 10.1021/nn302782y
-
[48]
Li M., Yang X., Ren J.. Using grapheneoxide highnear-infrared absorbance for photothermal treatment of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2012,24:1722-1728.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201104864
-
[49]
Kim C., Favazza C., Wang L.V.. In vivo photoacoustic tomography of chemicals:high-resolution functional and molecular optical imaging at new depths[J]. Chem. Rev.,
2010,110:2756-2782.
doi: 10.1021/cr900266s
-
[50]
Chen M., Tang S., Guo Z.. Core-shell Pd@Au nanoplates as theranostic agents for in-vivo photoacoustic imaging CT imaging, and photothermal therapy[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2014,26:8210-8216.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201404013

 Login In
Login In

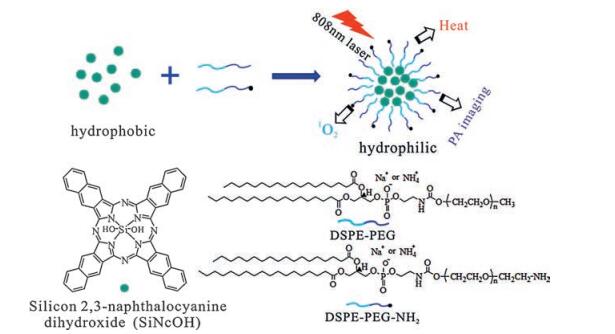





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: